3622: Check Divisibility by Digit Sum and Product
Problem Statement
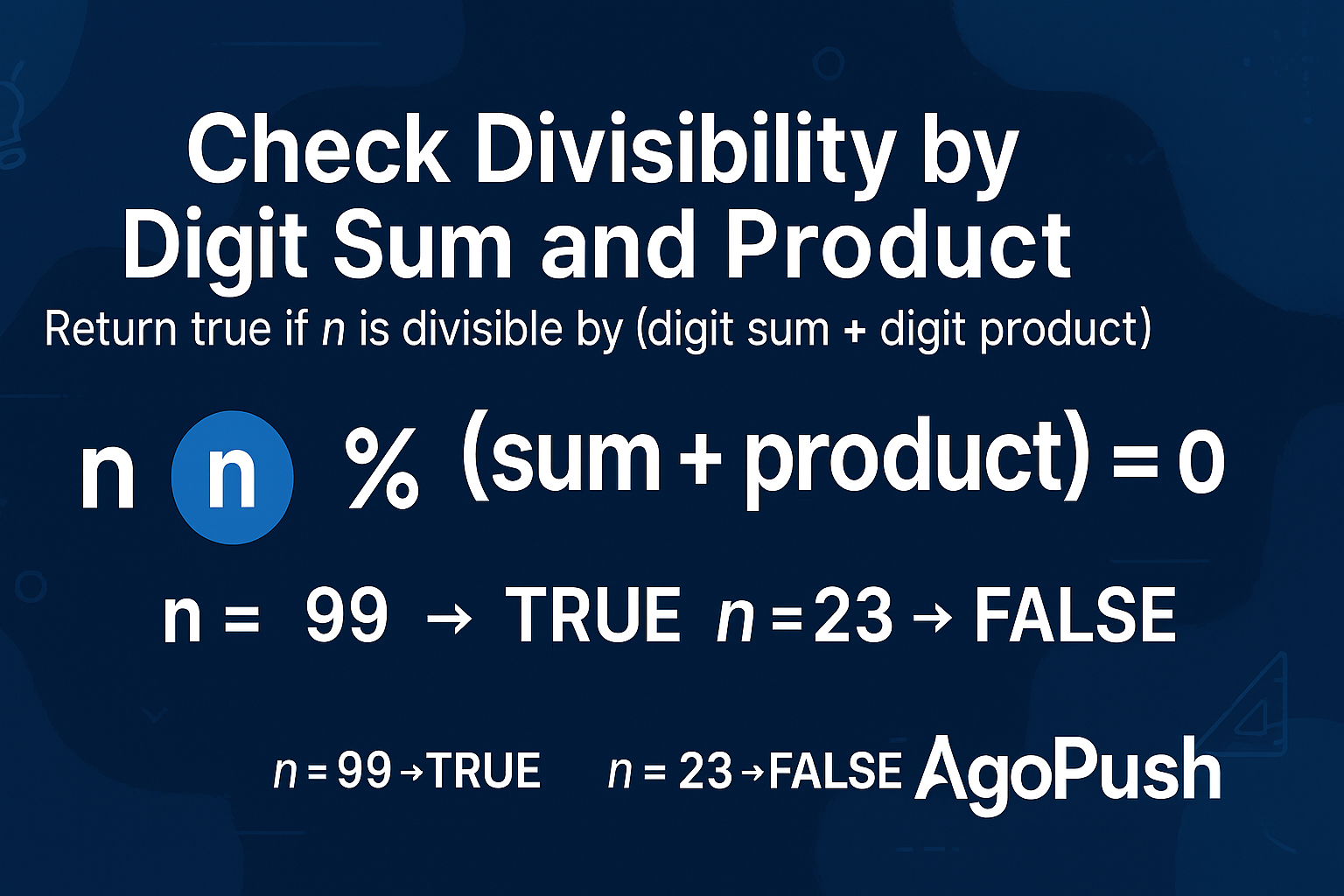
Given a positive integer n, determine if n is divisible by the sum of its digit sum and
digit product. Return true if divisible, otherwise false.
Formally: Let S = sum of digits of n, P = product of digits of
n. Return true if n % (S + P) == 0.
Example 1
Input: n = 99
Calculation: S = 9+9 = 18, P = 9×9 = 81, S+P = 99
99 % 99 = 0 → Output: true
Example 2
Input: n = 23
Calculation: S = 2+3 = 5, P = 2×3 = 6, S+P = 11
23 % 11 = 1 → Output: false
Key Insight
The problem requires:
- Extracting each digit from the number
- Calculating the sum of the digits (S)
- Calculating the product of the digits (P)
- Checking divisibility: n % (S + P) == 0
Approach 1: Modulus Digit Extraction
Extract digits using modulus and division operations.
Algorithm Steps
- Initialize
sum = 0andproduct = 1 - Make a copy of
n(to preserve original value) - While the number > 0:
- Extract last digit:
digit = num % 10 - Add digit to
sum - Multiply digit with
product - Remove last digit:
num = num / 10
- Extract last digit:
- Compute
total = sum + product - Check if
n % total == 0
Complexity Analysis
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|
| O(d) | O(1) |
Where d is number of digits in n. Since n ≤ 10^6, d ≤ 7.
class Solution {
public:
bool checkDivisibility(int n) {
int num = n;
int sum = 0;
int product = 1;
while (num > 0) {
int digit = num % 10;
sum += digit;
product *= digit;
num /= 10;
}
int total = sum + product;
return (n % total == 0);
}
};class Solution {
public boolean checkDivisibility(int n) {
int num = n;
int sum = 0;
int product = 1;
while (num > 0) {
int digit = num % 10;
sum += digit;
product *= digit;
num /= 10;
}
int total = sum + product;
return (n % total == 0);
}
}class Solution:
def checkDivisibility(self, n: int) -> bool:
num = n
digit_sum = 0
product = 1
while num > 0:
digit = num % 10
digit_sum += digit
product *= digit
num //= 10
total = digit_sum + product
return n % total == 0Approach 2: String Conversion Method
Convert number to string and process each character.
Algorithm Steps
- Convert integer
nto string - Iterate through each character in the string:
- Convert char to digit
- Add digit to
sum - Multiply digit with
product
- Compute
total = sum + product - Check if
n % total == 0
Complexity Analysis
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|
| O(d) | O(d) |
Where d is number of digits. Conversion to string requires O(d) space.
class Solution {
public:
bool checkDivisibility(int n) {
string num_str = to_string(n);
int sum = 0;
int product = 1;
for (char c : num_str) {
int digit = c - '0';
sum += digit;
product *= digit;
}
int total = sum + product;
return (n % total == 0);
}
};class Solution {
public boolean checkDivisibility(int n) {
String num_str = Integer.toString(n);
int sum = 0;
int product = 1;
for (char c : num_str.toCharArray()) {
int digit = c - '0';
sum += digit;
product *= digit;
}
int total = sum + product;
return (n % total == 0);
}
}class Solution:
def checkDivisibility(self, n: int) -> bool:
num_str = str(n)
digit_sum = 0
product = 1
for char in num_str:
digit = int(char)
digit_sum += digit
product *= digit
total = digit_sum + product
return n % total == 0Approach 3: Functional Programming Style (Python)
Use Python's functional programming features for concise implementation.
Algorithm Steps
- Convert number to string
- Map each character to integer digit
- Compute sum using
sum() - Compute product using
reduce()with multiplication - Check divisibility condition
Complexity Analysis
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|
| O(d) | O(d) |
Same as string conversion method but more concise.
from functools import reduce
import operator
class Solution:
def checkDivisibility(self, n: int) -> bool:
digits = [int(d) for d in str(n)]
digit_sum = sum(digits)
# Handle case with zero digits
product = reduce(operator.mul, digits, 1)
total = digit_sum + product
return n % total == 0reduce function elegantly handles product calculation.
Edge Cases and Testing
1. Single Digit Numbers
Input: n = 5 → Output: false
Calculation: S=5, P=5, total=10 → 5%10=5 (not 0)2. Numbers with Zero Digits
Input: n = 100 → Output: true
Calculation: S=1+0+0=1, P=1*0*0=0, total=1 → 100%1=03. Numbers with One Zero Digit
Input: n = 10 → Output: true
Calculation: S=1+0=1, P=1*0=0, total=1 → 10%1=04. All Digits Zero
Input: n = 0 → Output: undefined (n≥1 per constraints)5. Large Numbers
Input: n = 999999 → Output: false
Calculation: S=54, P=531441, total=531495 → 999999 % 531495 = 468504 (not 0)Frequently Asked Questions
1. What if the product of digits is zero?
This is perfectly valid. The total becomes (sum + 0) = sum. The divisibility check then becomes n % sum == 0.
2. Can the total (sum+product) be zero?
No. Since n ≥ 1, at least one digit is ≥1, making sum ≥1. Therefore, total = sum + product ≥1.
3. How to handle negative numbers?
The problem states n is positive, so negative cases don't need to be handled.
4. Why does modulus approach work better?
Modulus avoids string conversion and has O(1) space complexity vs O(d) for string methods.
5. What's the maximum number of digits?
For n ≤ 10^6, maximum digits is 7 (e.g., 9,999,999).
6. How does the product initialization work?
Product must be initialized to 1 because multiplying by 1 is the multiplicative identity. Initializing to 0 would make the entire product zero.
7. What if a number has leading zeros?
Numbers don't have leading zeros in their decimal representation. For example, 001 is stored as 1.
8. Is there a mathematical formula?
No direct formula exists. Digit extraction is required for each number.
9. Can we use logarithms to count digits?
Logarithms can count digits but don't help with extracting individual digits. Stick to modulus or string methods.
10. What are common mistakes?
Common mistakes: initializing product to 0, not preserving original n value, and not handling zero digits correctly.